The world just experienced its warmest March on record, capping a 10-month streak in which every month set a new temperature record, the European Union's climate change monitoring service said on Tuesday.
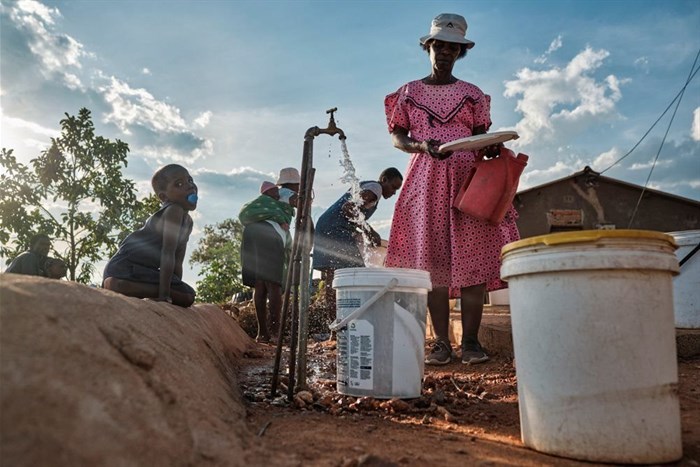

Residents queue to collect water, as temperatures soar during an El Nino-related heatwave and drought affecting a large part of the country, in Bulawayo, Zimbabwe, 7 March 2024. Reuters/KB Mpofu/ File Photo
Each of the last 10 months ranked as the world's hottest on record, compared with the corresponding month in previous years, the EU's Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) said in a monthly bulletin.
The 12 months ending with March also ranked as the planet's hottest ever recorded 12-month period, C3S said. From April 2023 to March 2024, the global average temperature was 1.58 degrees Celsius above the average in the 1850-1900 pre-industrial period.
"It's the long-term trend with exceptional records that has us very concerned," C3S Deputy Director Samantha Burgess told Reuters.
"Seeing records like this - month in, month out - really shows us that our climate is changing, is changing rapidly," she added.
C3S' dataset goes back to 1940, which the scientists cross-checked with other data to confirm that last month was the hottest March since the pre-industrial period.
Already, 2023 was the planet's hottest year in global records going back to 1850.
Philip Kofi Adom 1 Mar 2024
Devastating impact
Extreme weather and exceptional temperatures have wreaked havoc this year.
Climate change-driven drought in the Amazon rainforest region unleashed a record number of wildfires in Venezuela from January-March, while drought in Southern Africa has wiped out crops and left millions of people facing hunger.
Marine scientists also warned last month a mass coral bleaching event is likely unfolding in the southern hemisphere, driven by warming waters, and could be the worst in the planet's history.
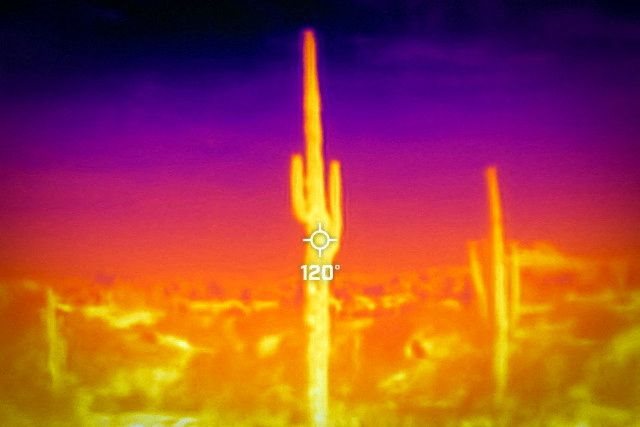

A saguaro cactus is seen during a 27-day-long heat wave with temperatures over 110 degrees Fahrenheit (43 degrees Celsius) at the Desert Botanical Garden in Phoenix, Arizona, US, 26 July 2023. On 26 July at 09.50am (GMT-7), a Flir One ProThermal camera registered a surface temperature of 120 degrees Fahrenheit (48 degrees Celsius), with an air temperature of 86 degrees Fahrenheit (30 degrees Celsius) according to the National Weather Service. Reuters/Carlos Barria/File Photo
The primary cause of the exceptional heat were human-caused greenhouse gas emissions, C3S said. Other factors pushing up temperatures include El Nino, the weather pattern that warms the surface waters in the eastern Pacific Ocean.
El Nino peaked in December-January and is now weakening, which may help to break the hot streak toward the end of the year.
But despite El Nino easing in March, the world's average sea surface temperature hit a record high, for any month on record, and marine air temperatures remained unusually high, C3S said.
"The main driver of the warming is fossil fuel emissions," said Friederike Otto, a climate scientist at Imperial College London's Grantham Institute.
Failure to reduce these emissions will continue to drive the warming of the planet, resulting in more intense droughts, fires, heat waves and heavy rainfall, Otto said.




























![Today, Halo and Demographica announce a new specialist agency, Second Rodeo]], headed up by Mike Stopforth (left). Dean Oelschig, managing partner and founder of Halo (right) says they will work as a group but ultimately, each agency will be an individual specialist](https://biz-file.com/c/2505/772543-64x64.jpg?2)






